MUC1-C induces DNMT1 expression by an NF-κB p65 dependent mechanism.... | Download Scientific Diagram

DNMT1-mediated lncRNA MEG3 methylation accelerates endothelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic retinopathy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway | American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism

NCL modulates DNMT1 expression via NFκB pathway. A, Kasumi-1 or MV4-11... | Download Scientific Diagram

Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of immune tolerance: roles of the NF-κB family members | Cellular & Molecular Immunology
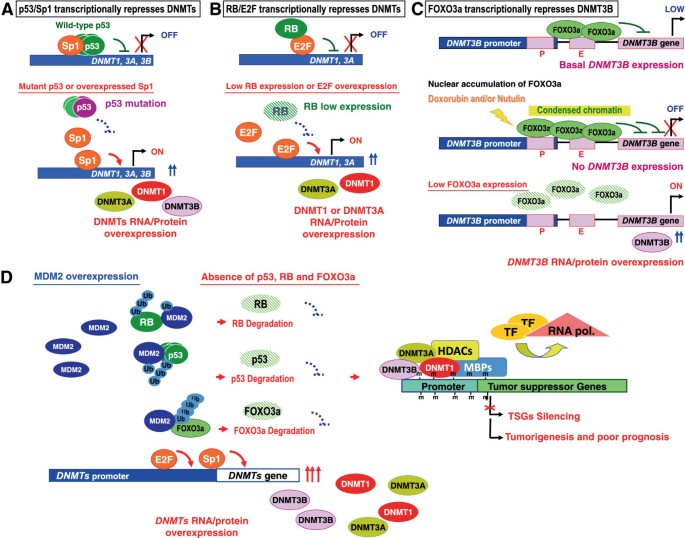
Dysregulated transcriptional and post-translational control of DNA methyltransferases in cancer | Cell & Bioscience | Full Text
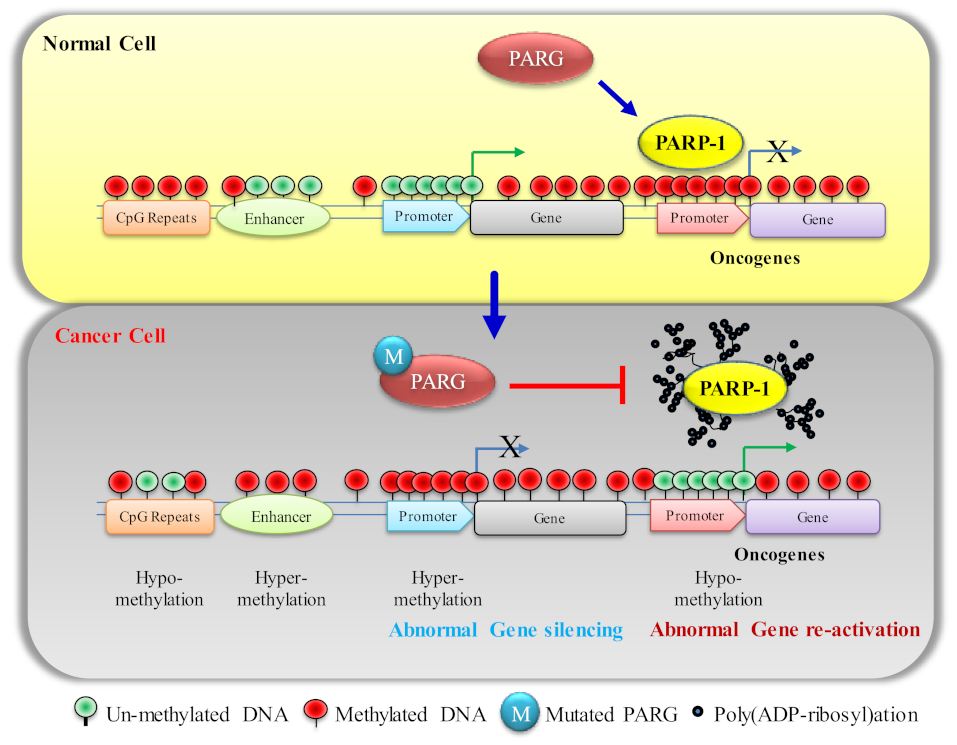
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | DNA Methylation Malleability and Dysregulation in Cancer Progression: Understanding the Role of PARP1
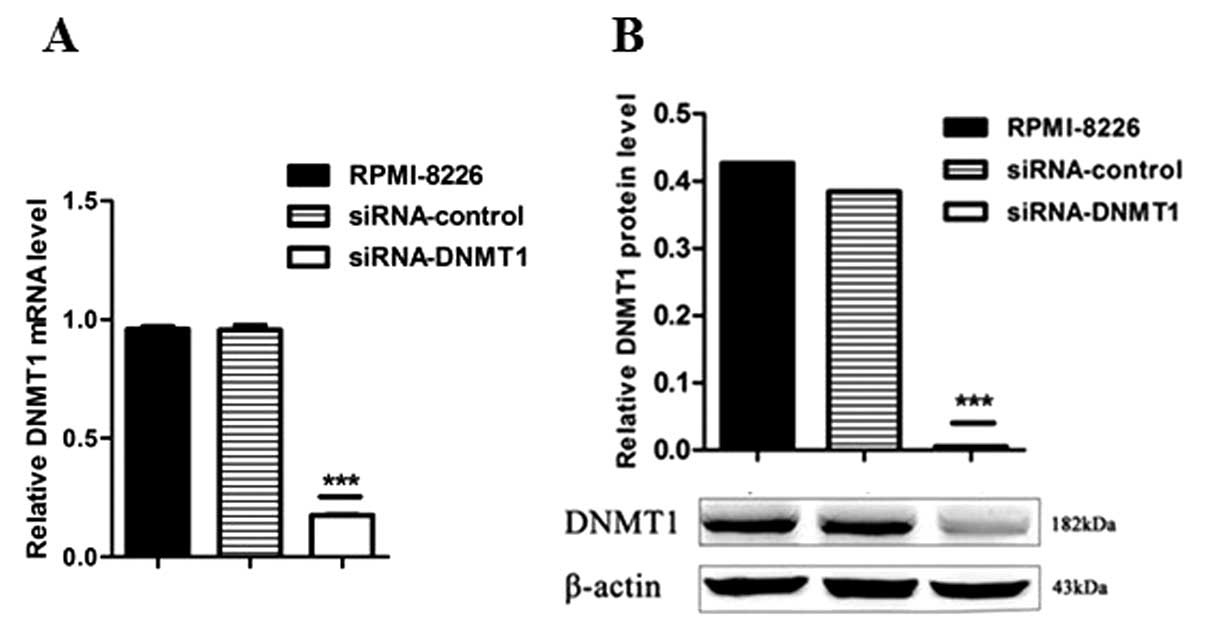
Knockdown of DNA methyltransferase‑1 inhibits proliferation and derepresses tumor suppressor genes in myeloma cells

MP99-04 TRUNCATED-CRMP4 BY CALPAIN-2 SUPPRESSES CRMP4 TO PROMOTE METASTASIS OF PROSTATE CANCER VIA PROMOTER METHYLATION THROUGH E2F1/NF-?B/DNMT1 SIGNALING | Journal of Urology

TGFβ1‐induced beta‐site APP‐cleaving enzyme 2 upregulation promotes tumorigenesis through the NF‐κB signalling pathway in human gliomas - Wang - 2020 - Molecular Oncology - Wiley Online Library

The role and regulatory mechanism of IL‐1β on the methylation of the NF2 gene in benign meningiomas and leptomeninges - Wang - 2016 - Molecular Carcinogenesis - Wiley Online Library

Regulation of Nuclear Factor-KappaB (NF-κB) signaling pathway by non-coding RNAs in cancer: Inhibiting or promoting carcinogenesis? - ScienceDirect

The interaction between miRNAs/lncRNAs and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) in human disorders - ScienceDirect
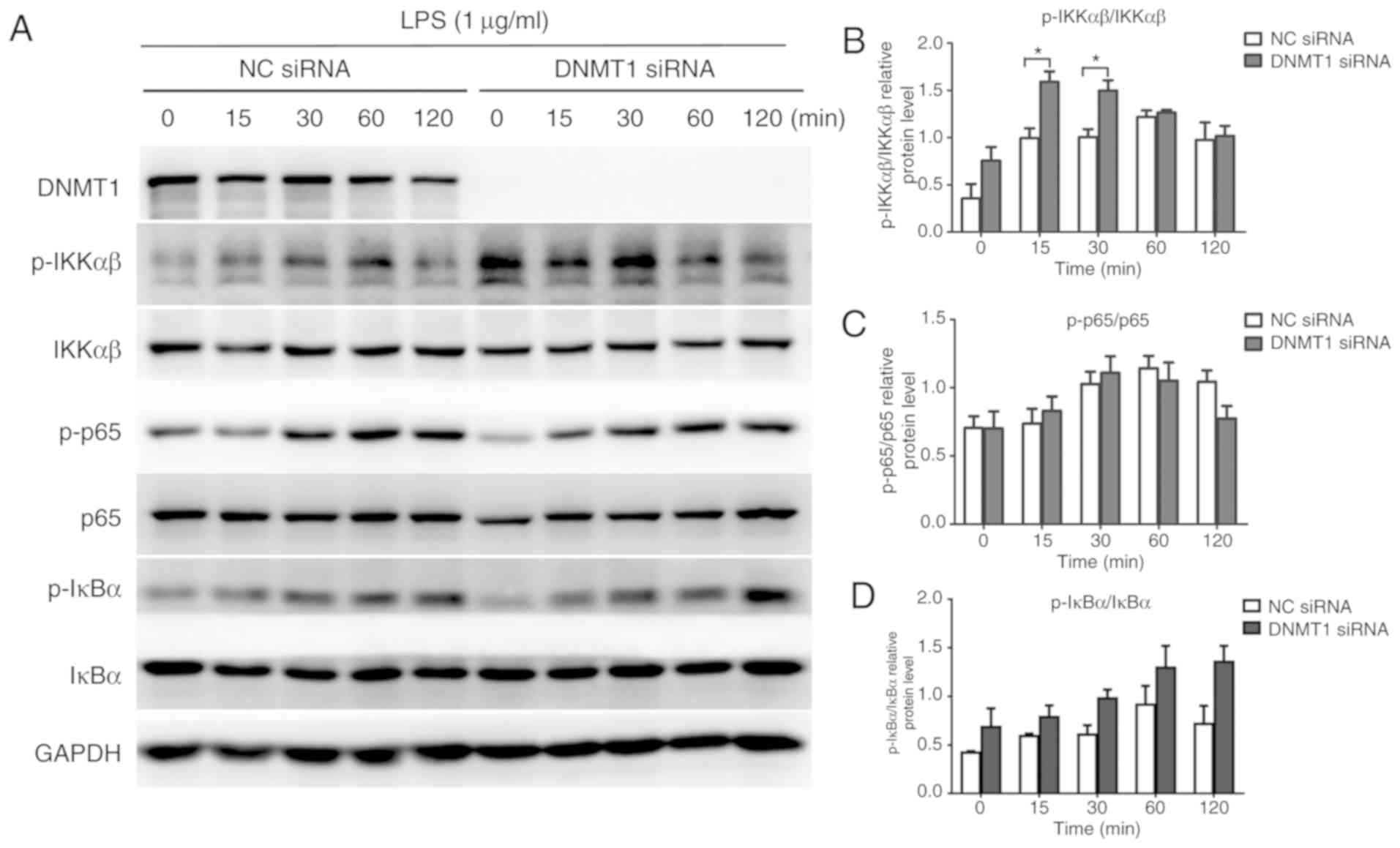
DNA methyltransferase DNMT1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide‑induced inflammatory response in human dental pulp cells involving the methylation changes of IL‑6 and TRAF6
DNA methyltransferase 1 may be a therapy target for attenuating diabetic nephropathy and podocyte injury

Expanding the MECP2 network using comparative genomics reveals potential therapeutic targets for Rett syndrome | eLife

Regulation of DNA methylation machinery by epi-miRNAs in human cancer: emerging new targets in cancer therapy | Cancer Gene Therapy